Thermal imaging cameras used to be reserved for military and specialist business operations.
Now, they’re accessible to everyone in various budgets, designs, and specs to fit all needs. That’s why I scouted the market for you and crafted this list with the nine best thermal imaging cameras in 2024.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
High resolution, excellent thermal sensitivity, user-friendly interface, durable build, and additional useful features like MSX imaging.
If you landed on this article out of curiosity but are not on the hunt for a thermal camera, stick around. At the end of the article, I’ll tell you what thermal cameras are and how they work. I’ll also give you some practical and fun ways to use them.
But suffice to say, they can be used in specific occupations, for educational purposes, and are a valuable tool around the home.
For now, let’s look at some of the best thermal imaging cameras on the market right now.
What is the Best Thermal Imaging Camera in 2024?
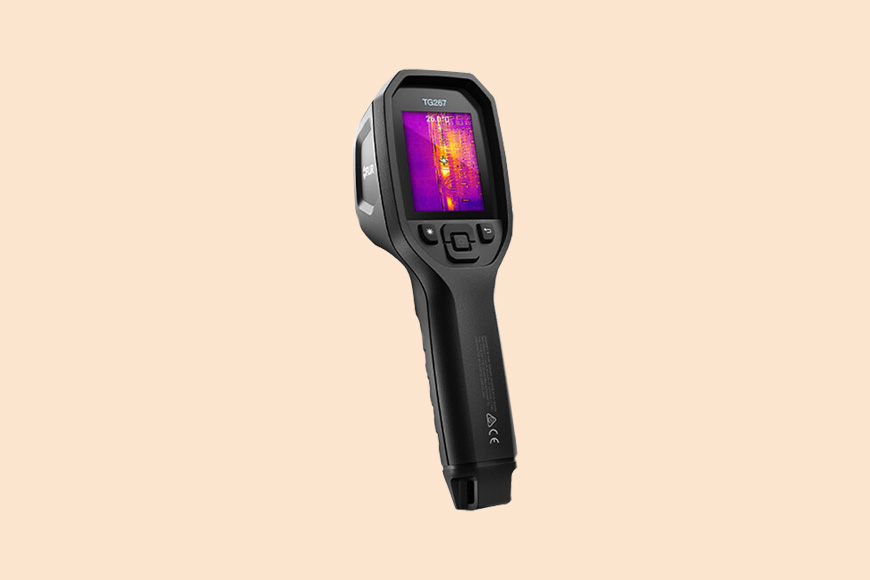
FLIR TG267 (Overall Best Infrared Camera for Thermal Imaging)
- Great image quality
- Robust
- 5 hours of continuous use
- Easy to use
- Relatively expensive for amateur use
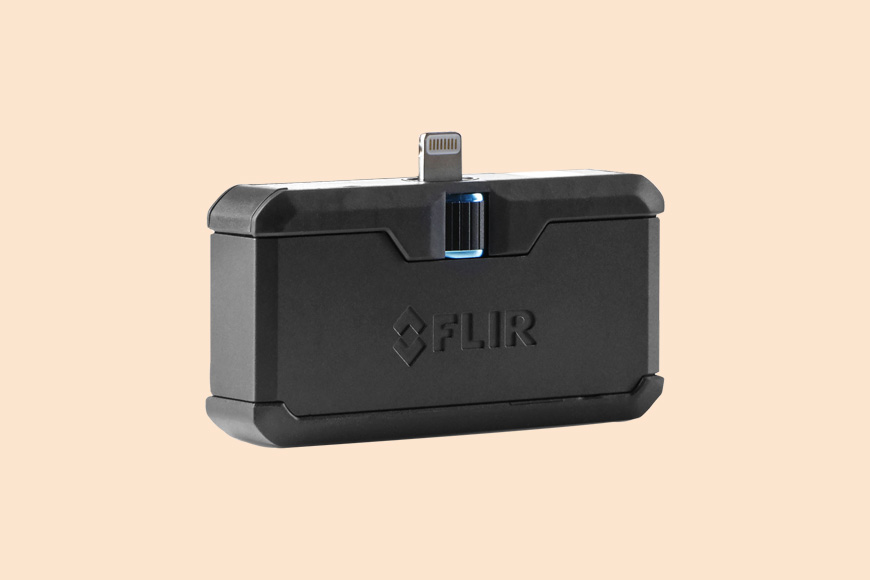
The FLIR TG267 is a great, no-nonsense thermal imaging camera that’s easy to configure and can be used straight out of the box.
The camera enclosure is IP54 rated, protected from dust and water, and can withstand a drop of 2m and temperatures ranging from -25°C to 380°C. This, as well as its other features, makes it the best thermal imager on the list.
FLIR’s own MSX technology superimposes a digital image over the thermal one to give you exceptional image clarity on its 2.4-inch LCD screen.
Plus, you can store up to 50,000 images on the device if you need to, images that can also be transferred to your computer either wirelessly or using a USB-C cable.
This thermal camera has a laser bullseye that helps you pinpoint exactly what you want a reading of. It also comes with a thermocouple probe for more accurate readings when checking heating, ventilation, or air conditioning systems.
While it’s not the newest camera, it’s still a solid option for those who are looking for an affordable and versatile handheld camera. However, if you’re looking for a higher resolution, try the HIKMICRO20 for a similar price.
Seek Thermal ShotPRO (Best Mid-Range Handheld)
- Tiny, tough, and feature-packed
- Great image quality
- 4 hours battery life
- Many advanced settings for calibration
- Zoom settings are a bit fiddly
- Frontal LED light is too dim
In a prior version of this list, I recommended the Seek Thermal Reveal Pro as the best mid-range thermal imaging camera. Unfortunately, this is no longer in production.
I was torn between recommending the Seek Thermal Reveal 300 or the ShotPRO as its replacement. I finally decided to go with the ShotPRO. This is partly because it’s much more affordable.
It’s not just about the price, though. The Seek Thermal Shot PRO is a compact, lightweight device packed with a high-resolution sensor with 76,800 pixels.
Among the key features is its capability to capture, analyze, and edit photos. Not only that, it also has WiFi, which allows you to stream live video via the free SeekView app. The housing has a tripod mount to improve the quality of your stream and free your hands.
It has a large 3-5″ touch-screen display, and for better visibility, you can adjust the blend between the thermal and visible images using SeekFusion.
The battery life is roughly 4 hours, and it has an internal memory of 4GB. You’ll find that this small yet durable camera is top-of-its-class.
However, you may prefer the Reveal 300 if you prefer a hand-held flashlight design or when you need to detect higher temperatures. Please note that neither of these models is suitable for firefighting – for that, please look at the FIREPRO series.
Hti-Xintai HT-18 (Best Budget Thermal Camera)
- Compact
- Good range of features
- Affordable price point
- Instruction manual is basic, so you’ll need to research
If you want the best cheap thermal camera, check this one out.
This compact, chargeable, handheld thermal imaging camera is a good option for those not wanting to break the bank.
It has two cameras, a visible light camera and a thermal imaging camera. You can change how much of the thermal image overlays the visible light image in increments.
It’s also possible to slightly offset the two images, which could be quite helpful to pinpoint the source of, for example, a heat leak you’re researching.
Despite its low price, the Hti-Xintai HT-18 still has a good range of sophisticated features you’d expect to find on more expensive thermal cameras. This makes it the best budget thermal imaging camera among the others on the list.
For example, you can set your colour palette, and custom set the emissivity rating (useful if you’re using the device on different surfaces).
For a cheap thermal camera, this one’s really hard to beat when you’re on a tight budget.
Seek Thermal Compact Pro (Best for iPhone/Android)
- Extremely compact
- Doesn’t need charging
- Works straight from a phone
- High-resolution thermal imagery
- Lens focusing can be sticky
- Pretty expensive
- No waterproofing
This is the top pick for the best thermal camera for Android and iPhone.
This is an interesting little device. Unlike other visible light cameras in this guide, there’s no need to charge it as a mini-USB-C connection from your phone powers it.
At this price point, it has one of the highest thermal imaging resolutions (320 x 240) on the market.
It also has the functionality to make important thermal adjustments, like emissivity (adjusting for material properties) and span and level (which fine-tune the temperature range and focus of the displayed thermal image for greater accuracy).
Before purchasing, though, something to note is that you might need an adaptor to use it, depending on the thickness of your phone and whether or not you use a phone protector.
Also, it’s on sale right now at Thermal.com, so you can save 20% off the normal retail price.
If you need a longer detection distance, try the CompactPRO XR, although it’s only available for USB-C Android phones.
FLIR Scout TKx Compact (Best for Hunting)
- Great features for the price
- Comfortable eye rest
- Simple to learn and use
- Different color palettes
The FLIR Scout TKx Compact is a pocket-sized thermal monocular that can be used to track animals up to 100 yards (90m) away.
That animal could be your pet in the garden after dark, game you’re hunting in the great outdoors, or game you’ve already hunted and now need to find and harvest.
It’s also popular as a handy way to see your opponent when playing paintball in the dark.
In fact, thermal cameras have been used by the US Military and Police forces for years.
As you’d expect from something made for the outdoors, it has a sleek but rugged build tested to IM-67 submersible waterproof standard. The rubber-molded coating makes it comfortable to hold and shock-resistant up to around 2 meters.
It has a rechargeable battery that lasts up to seven hours.
FLIR One Gen 3 (Best Value)
- Compact
- Easy to fit to phone
- Simple app
- Good features for the low price
Similar to the Seek Thermal Compact Pro, this is one of the daintier imaging cameras out there, made to attach to your phone.
Unlike the Seek camera, there’s no need for an adaptor to fit it to your phone even if your phone is bulky or you have a thick protector; a thumbwheel adjusts the length of the micro-USB-C.
It has two cameras: a visible light camera and a thermal camera. The visible light camera’s high pass filter provides a constant outline beneath the thermal image, so you always know exactly what you’re looking at.
The app is easy to use and with it, you can make the kind of adjustments – emissivity, palette – that will help you get the most out of it.
If you need more resolution and you can add an extra $50 to $100, you can check out the TOPDON TC001.
BOSCH GTC400C (Best for Pros)
- Fast, responsive measurements
- Robust build
- Software for report creation
- Expensive
- Should come with a hard case
The BOSCH GTC400C is a professional piece of equipment with a price tag to match.
Most home users won’t need it, but if this is what you need at work, it will have all the features to carry out the job.
Its ergonomic design makes it easy to hold for long periods, and the large screen is easy on the eyes.
It measures temperatures extremely quickly and displays them in a three-crosshair system. One crosshair is fixed in the center of the image, and the other two float, focusing on the hottest and coldest objects on the screen.
You then have the full range of features – emissivity, transparency settings, palette selection, and more – to help you fine-tune the thermal camera’s output to your needs.
Files can be transferred wirelessly to your phone or by USB-C cable to your computer.
Once on your computer, you can use BOSCH’s powerful GTC Transfer Software to create and annotate detailed visual reports.
Pro tip: the BOSCH GTC400C’s Lithium-ion battery compartment is the same as for BOSCH power tools – they’re interchangeable. So, if you’re traveling with a toolkit, it’s an easy way to have backup batteries around.
FLIR One Pro
- Easy to mount on a phone
- Built-in battery
- Good resolution
- None (it should be clear now that I’m a fan of these little FLIRs)
Another FLIR option that will attach to your phone.
It’s virtually identical in build, features, and operation to the cheaper FLIR One Gen 3, but there are some important differences.
The FLIR One Gen 3 can detect temperatures of between -20 and 120°C, and has less thermal sensitivity (150 mK). In contrast, the FLIR One Pro can detect temperatures of between -20 and 400 degrees°C, and has greater thermal sensitivity (70 mK).
The thermal resolution on the FLIR One Pro is double that of its cheaper sibling, which means much higher image quality.
The FLIR One Pro also has an internal battery, so you can use it for much longer.
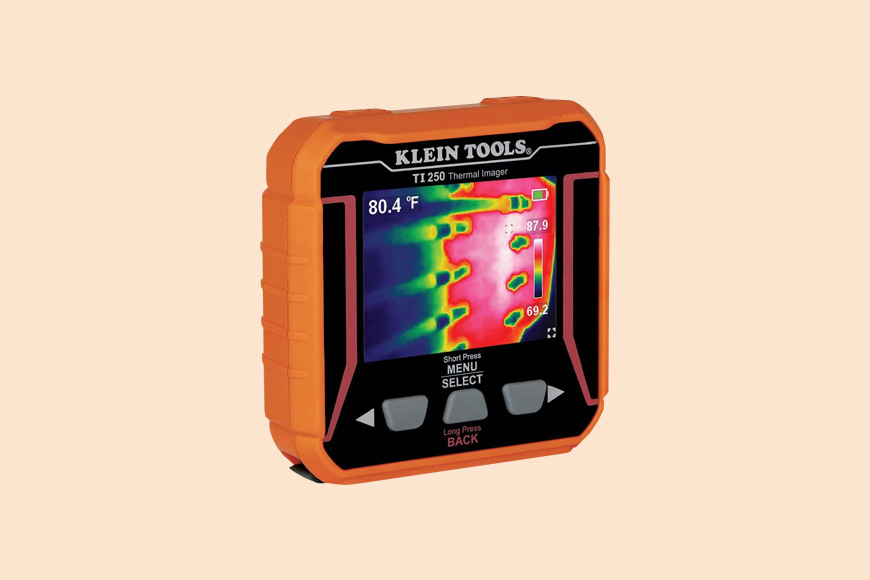
Klein Tools TI250
- Rugged
- Compact
- Good image quality
This bright orange tool has 10,000 pixels of resolution and can measure temperatures from -40 to 250°C.
It’s covered in rubberized heavy-duty plastic molding for protection, and at just over 3 inches in width and length, it’s compact enough for a tool kit.
There’s nothing new here when compared to the other cameras in this guide, but there doesn’t need to be. It has all the features you need, such as adjustable emissivity and color palette, from a thermal imaging camera at this price point.
Images are stored on a micro SD card and can easily be downloaded to your computer.
What Is a Thermal Imaging Camera Used for?
They’re used in professional environments by field technicians, firefighters, soldiers, and more.
For example, building inspectors use these cameras a lot. By looking at thermal images, they can spot where heat is leaking from a house or if there’s a spot that’s cooler than it should be. This can show if the house’s insulation is not working well, or if there’s a damp spot.
Electricians and mechanics also use thermal imaging devices. If a machine or electrical system is overheating, that could be a sign of a problem. The camera can help them spot the issue before it gets worse.
Police and firefighters find thermal imagers handy, too. Firefighters can see through smoke with them, which helps them find people faster in emergencies. Police use them to find people in the dark—the heat a person gives off is easy to see with the camera.
Doctors sometimes use thermal cameras to check blood flow in the body. If an area is hotter than normal, it might mean more blood is flowing there, which can help locate problems.
In the home, they’re useful for non-professionals, too. They can be used to find electrical faults and water leakage and locate studs or ceiling joists.
They’re also handy for security and home defense, and even finding dog poo when your pet has done their business in the dark!
In an educational context, they can be used for fun things like drawing with heat or mixing hot and cold water to see where the currents go.
10 Fun Uses for Thermal Cameras
Here are ten fun uses for a thermal imaging camera you might not have already thought of:
- Stargazing: They can be used for amateur astronomy to observe celestial bodies, especially during nights when the sky is filled with clouds.
- Ghost Hunting: Some people use thermal imaging cameras during ghost-hunting adventures. They hope to detect unusual cold spots that might indicate a spectral presence.
- Cooking: They can be used to check the heat distribution on a grill or pan to find the perfect cooking spot or to see if the cake is evenly cooked.
- Gardening: Use a thermal imaging camera to spot pests or diseases in your plants. Insects and diseases can affect the temperature of plants, making them visible in thermal images.
- Wildlife Spotting: If you like nighttime adventures, a thermal imaging camera can help you spot animals in the dark.
- Art: Some artists use them to create unique artwork based on heat patterns.
- Exploring Caves: Thermal imaging cameras can help you navigate dark caves and also help spot small animals hiding in the crevices.
- Bird Nest Spotting: You can use a thermal camera to locate bird nests without disturbing the surroundings.
- Fishing: Thermal cameras can be used to spot areas in a body of water where fish may be schooling.
- Finding Lost Pets: If your pet is hiding or lost at night, a thermal camera can help locate them by their heat signature.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Imaging Camera
As you can see from this guide, there are several camera levels: some for pros, some that are best for hunting, and some that can be used with a mobile phone.
When you’re choosing a thermal imaging camera, here are the criteria to think about:
- Resolution: This is one of the most important factors. The resolution of a thermal camera is stated in pixels. The higher the resolution, the better and more detailed the image quality. A low-resolution thermal camera may not capture the necessary detail for some uses.
- Sensitivity: Thermal sensitivity determines how small a temperature difference the camera can detect. A high thermal sensitivity allows you to detect smaller temperature differences, which could be crucial in applications like leak detection or insulation efficiency analysis.
- Temperature Range: The temperature range that the thermal camera can detect is crucial. If you’re working in extreme conditions, you’ll need a camera that can handle these temperatures.
- Field of View: Depending on your requirements, you may need a wide or narrow field of view (FOV). A wide FOV is beneficial for scanning large areas quickly, while a narrow FOV allows for more detail over longer distances.
- Refresh Rate: The refresh rate of a thermal camera determines how many images it can process per second. A higher refresh rate can give a smoother image, especially when you’re scanning a scene quickly or tracking a moving object.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface can save time and make the camera easier to operate. Check the software and consider if you prefer a camera that is stand-alone or one that requires a smartphone or tablet to operate.
- Durability: Depending on your working conditions, you may need a thermal imaging camera that’s water-resistant, dust-proof, or able to survive a fall.
- Extra Features: Other features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, integrated visual camera, image fusion (overlay of thermal and visual image), video recording, and adjustability of emissivity can be useful depending on your specific needs.
- Price: The cost of the camera can vary significantly, with professional-grade cameras costing significantly more than entry-level models. Consider your budget and the features you need to find a camera that offers the best value for your money.
- Support and Warranty: Look at the warranty period and the manufacturer’s reputation for customer support. Having access to software updates, customer service, and potential repairs can be very helpful.
How Do Thermal Imaging Cameras Work?
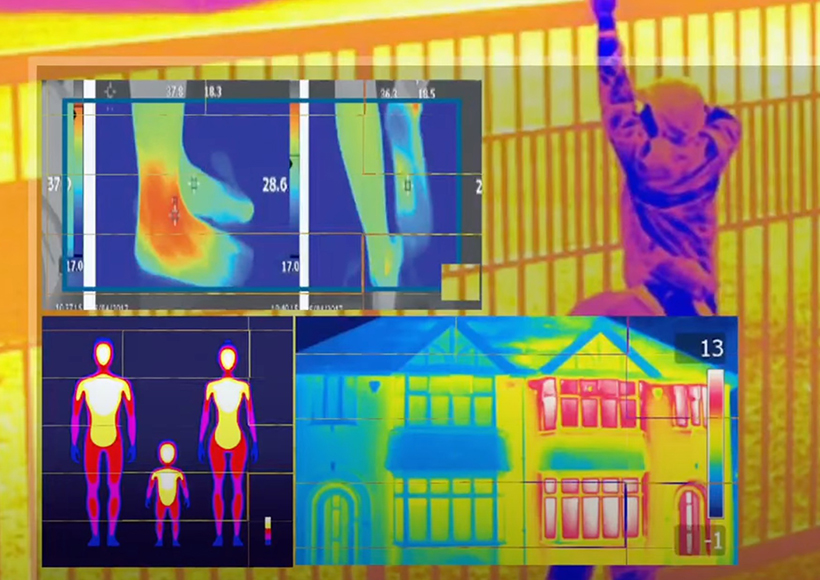
A thermal imaging camera is a special camera that lets you see heat. Just like we see light with our eyes, this camera can see heat, which we normally can’t see.
The way it works is pretty cool. When you point it at something, it catches the heat coming off that thing. The camera’s lens focuses this heat onto a special sensor inside.
Each tiny part of that sensor measures the heat it catches and assigns a color to it. So, different temperatures get different colors. This creates a picture made up of colors showing how hot or cold everything is.
The camera then turns this information into an image you can see on a screen. This picture is usually bright in hot areas and dark in cool areas, giving you a ‘heat map.’
What Is Infrared Radiation and Why Is It Important to Thermal Images?
Infrared radiation is actually a big part of how thermal cameras work.
It’s a kind of energy we can’t see with our eyes, but we can feel as heat.
Every object that’s not super, super cold gives off some infrared radiation. The hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it gives off.
This is where the thermal camera comes in. It’s like it has superpowers because it can see this invisible infrared radiation.
When you point the camera at something, it catches the infrared radiation coming from that object. It’s a bit like catching a ball, but instead of a ball, it’s catching heat energy.
Once the camera has caught this infrared radiation, it measures how much heat there is and then shows it as a picture.
The camera uses different colors to show different amounts of heat, making it easy for us to understand.
So, in short, without infrared radiation, thermal cameras wouldn’t work. They’re specially designed to see this invisible heat energy that every object gives off.
How do you ‘Read’ an Infrared Image?
In the infrared image, each color represents a different temperature. Hot things are usually shown in bright red, orange, or white colors. Cold things are shown in cool colors like blue, green, or black.
Things between hot and cold would be shown in colors like yellow or light green.
Let’s say you’re looking at a thermal image of a dog. You might see its nose in blue because it’s cooler, and its body in red because it’s warmer.
Sometimes, thermal cameras will show a scale on the side of the image. This scale will tell you which colors represent which temperatures, so you know exactly how hot or cold things are.
Reading a thermal image can take a bit of practice, but once you get the hang of it, it’s pretty cool to see the world in a whole new way.
All the best thermal cameras in this guide create infrared images to show hot and cold spots.
Thermal Imaging Cameras: FAQs
Can I use my phone as a thermal camera?
Yes, you can. Several thermal imaging cameras in this guide plug directly into both Android and iOS smartphones.
What is the difference between an infrared camera and a thermal camera?
They are different ways of saying the same thing. A thermal camera reads the light you cannot see. That light is infrared and radiates from the surface of any material. The warmer that material is, the more infrared it radiates. Each pixel of a thermal camera is an infrared temperature sensor, so you get the temperature of thousands of points simultaneously.
A thermal camera uses an infrared sensor, so it is an infrared camera.
What is the best thermal camera for house inspection?
If you’re doing this as a job, you’ll probably want to get the BOSCH GTC400C.
For homeowners, one that attaches to your phone is probably enough. So, FLIR One Pro, the FLIR One Gen 3, or the Seek Thermal Compact Pro.
What is the highest-resolution thermal camera?
Out of the cameras in this guide, the Seek Thermal ShotPro and the Seek Thermal Compact Pro, at 320 x 240 have the highest resolutions.
But remember, resolution is not the only important metric when buying a thermal imaging camera. You also need to consider the camera’s thermal sensitivity and frame rate.
Can a thermal imaging camera detect water leaks?
Yes, it can.
What is the best thermal camera for firefighting?
The FLIR K55 (not in this guide) is made specifically for this purpose, but it’s pricey. Also, Seek Thermal has a FirePRO line.
What is multi-spectral dynamic imaging?
It combines the thermal image with a regular, visible light image to create a detailed picture that’s much easier to understand. It takes the detail from the visible light picture and overlays it onto the thermal image. This means you can see both the heat and all the fine details in the same picture.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
High resolution, excellent thermal sensitivity, user-friendly interface, durable build, and additional useful features like MSX imaging.
Credit : Source Post











